Breast Anatomy
The structure of the breast
Breasts are made up of breast tissue (also called glandular tissue) and fat, along with nerves, veins, arteries, and connective tissue that helps hold everything in place.
Breast tissue is a complex network of lobules (small round sacs that produce milk) and milk ducts (canals that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple openings during breastfeeding) in a pattern that looks like bunches of grapes. These “bunches” are called lobes.
The main chest muscle (the pectoralis muscle) is found between the breast and the ribs in the chest wall.
The following is a 3D interactive model showing breast anatomy. The labels highlight different parts of the breast.
The female breast
Changes during childhood and the teen years
Throughout childhood, girls have a small patch of immature breast tissue.
During puberty, hormones produced by the ovaries and pituitary gland (a part of the brain that controls growth and other glands in the body) cause the breasts to grow. This causes the milk ducts to stretch out and become more branched.
The breast tissue then develops into a mature system of lobules and ducts.
The adult breast
Adult women have 15-20 lobes in each breast [1]. Each lobe has 20-40 lobules [2].
Small milk ducts are attached to the lobules. These ducts join together like branches of grape stems, gradually forming larger ducts.
There are about 10 duct systems in each breast, each with its own opening at the nipple [2].
Though the breast is mature after puberty, the breast tissue remains inactive until pregnancy.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy, the lobules grow and begin to produce milk. The milk is then released into the ducts so a mother can breastfeed her baby.
Muscle tissue in the nipples allows them to become erect in response to stimulation or breastfeeding. Muscle tissue around the lobules helps squeeze milk into the ducts.
Glands on the areola (the shaded circle of skin around the nipple) release small amounts of fluid during breastfeeding to lubricate the nipple.
Changes after menopause
After menopause (when the ovaries stop producing hormones and a woman stops having periods), the number of lobules decreases and those that remain shrink in size.
As breast tissue decreases during menopause, breast density may also decrease.
- Before menopause, the breasts have more breast tissue than fat (higher breast density).
- After menopause, the breasts typically have more fat than breast tissue (lower breast density).
This natural change in breast density makes it easier to read a woman’s screening mammograms after menopause [3].
Learn more about breast density and mammography.
Learn about breast density and breast cancer risk.
The male breast
Boys and girls begin life with similar breast tissue. However, men don’t have the same complex breast growth and development as women.
At puberty, high testosterone levels and low estrogen levels stop breast development in men.
Men have some milk ducts, but they remain undeveloped. Lobules are most often absent.
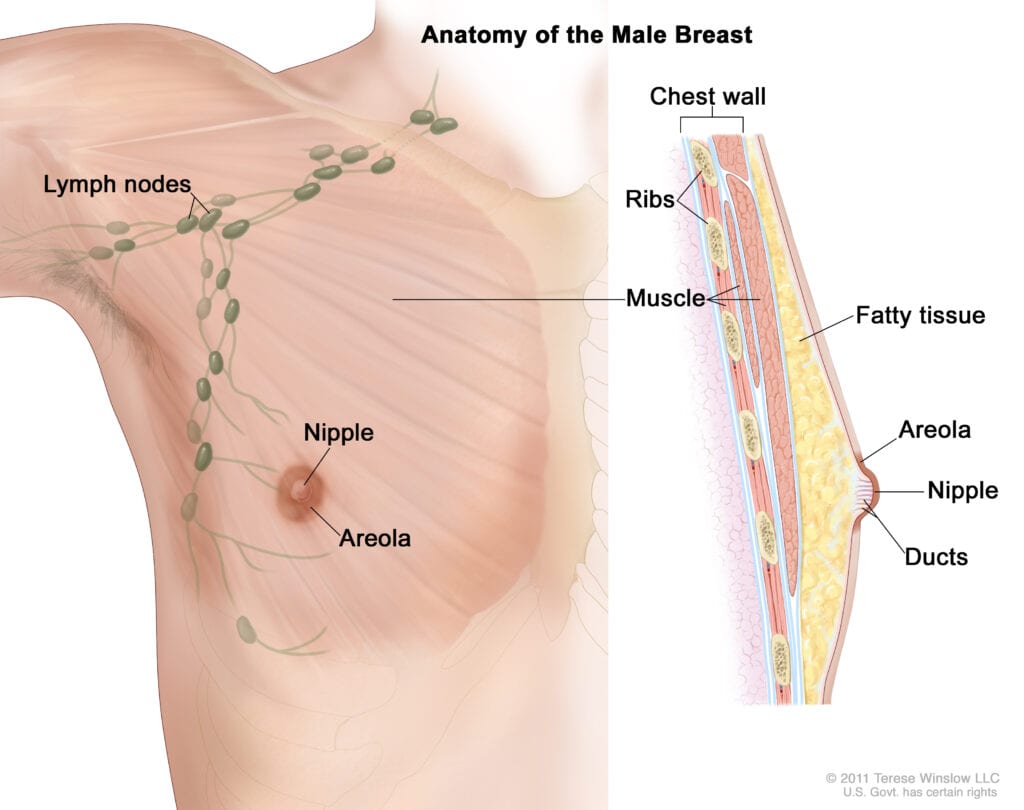
Learn about male breast cancer.
Updated 03/15/24
TOOLS & RESOURCES

In Your Own Words
How has having breast cancer changed your outlook?


